What Is Ginger’s Impact on Heart Health?
Ginger plays a crucial role in supporting heart health by addressing several key risk factors, including high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar levels, and high LDL cholesterol. These factors are known contributors to cardiovascular disease, making ginger a valuable addition to a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Research indicates that ginger can aid in blood pressure regulation. The bioactive compounds in ginger, such as gingerol, have been shown to improve circulation and relax blood vessels, promoting more efficient blood flow. This action helps in reducing hypertension, which is a significant risk factor for heart disease. A 2019 meta-analysis of six randomized controlled trials(1) (345 participants) found that ginger supplementation at doses of ≥3 g/day for up to 8 weeks significantly reduced systolic blood pressure by an average of 6.4 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 2.1 mmHg.
In addition to its effects on blood pressure, ginger also helps reduce cholesterol levels. Studies have found that regular consumption of ginger can lead to a decrease in LDL cholesterol, commonly referred to as "bad" cholesterol. By lowering LDL levels, ginger reduces the buildup of plaque in arteries, thereby decreasing the risk of atherosclerosis and subsequent heart disease.
Ginger's impact on blood sugar regulation further underscores its cardiovascular benefits. By enhancing insulin sensitivity and glucose absorption, ginger helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, which is essential for preventing diabetes-related complications that can affect heart health.
The protective effects of ginger on heart health are supported by its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These properties help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which contribute to cardiovascular disease. By incorporating ginger into the diet, individuals can take proactive steps in managing heart health and reducing the risk of heart disease. Whether consumed fresh, as a supplement, or in tea, ginger offers a natural approach to supporting cardiovascular well-being.
How Can Ginger Enhance Digestive Health?
Ginger plays a pivotal role in enhancing digestive health, primarily by expediting stomach emptying and alleviating various forms of nausea. This makes ginger an invaluable tool for those experiencing digestive discomfort, whether from motion sickness, pregnancy-related morning sickness, or other causes. Numerous clinical trials have validated ginger's effectiveness in reducing nausea and vomiting, making it a reliable natural remedy. There is solid scientific evidence for this effect. A 2023 study published in BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies found that relapsing-remitting MS patients who consumed 1,500 mg of ginger daily for 12 weeks experienced significant improvements in constipation, bloating, and nausea (Foshati et al., 2023)(2). These results strongly support ginger’s regulatory effects on the digestive system.
Ginger's ability to improve gastrointestinal motility is well documented. By accelerating the passage of food through the stomach, ginger helps prevent bloating and discomfort, promoting a smoother digestive process. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions like dyspepsia, where slowed digestion can lead to significant discomfort.
Incorporating ginger into your diet can be done in several ways. Fresh ginger root can be added to teas and meals, providing both flavor and digestive benefits. For those seeking convenience, ginger supplements in capsule or powdered form offer an easy way to integrate ginger into daily routines. Ginger tea is another popular option, known for its soothing effects on the stomach.
The effectiveness of ginger in improving digestion is supported by clinical evidence. Studies have shown that even a small daily dose of ginger can have a significant impact on reducing nausea and enhancing digestive efficiency. This positions ginger as a natural alternative to over-the-counter anti-nausea medications, with the added benefit of being free from synthetic chemicals.
To leverage the full range of ginger root benefits for digestive health, consider combining ginger with other digestive aids such as peppermint or fennel. This combination can further enhance digestive comfort and overall gut health, providing a holistic approach to managing digestive issues effectively.
How Does Ginger Boost Your Immune System?
Rich in antioxidants, ginger plays a crucial role in immune system support. Its potent antimicrobial and antiviral properties make ginger a valuable ally in fending off colds and flu. By enhancing immune function, ginger helps maintain overall health and resilience against common illnesses.
Ginger's immune-boosting capabilities are attributed to compounds like gingerol, which actively combat pathogens and reduce inflammation. This not only aids in preventing infections but also supports recovery. By incorporating ginger into your daily routine, you can naturally enhance your body's defenses. While detailed human trials are still emerging, a 2022 review published in Frontiers in Nutrition(3) found that in vitro and in vivo studies consistently demonstrate how ginger’s bioactive compounds like 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol exert potent antioxidant effects and modulate immune responses by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway and reducing oxidative stress.
There are various ways to enjoy ginger for immunity. Fresh ginger can be added to meals, smoothies, or brewed as a tea, offering both flavor and health benefits. Ginger supplements, available in capsules or powders, provide a convenient method for consistent intake.
To maximize ginger's immune-boosting effects, consider pairing it with other immunity-enhancing foods such as lemon and honey. This combination not only tastes delightful but also provides a synergistic boost to your immune system, helping you stay healthy year-round.
What Is Ginger’s Role in Pain Reduction?
Ginger has gained recognition for its natural pain-relieving properties, offering a viable alternative to traditional pain medications. Studies indicate that consuming 2 grams of ginger daily for 11 days can significantly reduce exercise-induced muscle pain. This positions ginger as an effective option for athletes and individuals experiencing muscle soreness from physical activity.
The ginger health benefits extend to managing chronic pain conditions as well. Ginger's active compounds, such as gingerol, exhibit properties similar to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin. This makes ginger particularly effective in alleviating menstrual cramps, providing relief akin to over-the-counter pain relievers but without their potential side effects.
For those seeking to incorporate ginger for pain reduction, there are several practical options. Fresh ginger can be added to teas and meals, or consumed as ginger tea to soothe discomfort. Ginger supplements, available in capsule form, offer a convenient method for achieving a consistent daily intake of ginger's beneficial compounds. A 2025 randomized, double-blind trial(4) showed that a high-potency ginger extract (125–150 mg) reduced subjective muscle pain and inflammation markers in individuals with mild joint pain from physical activity. These findings align with ginger’s well-documented anti-inflammatory properties driven by compounds like 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol that help reduce pain perception naturally.
Research comparing ginger to traditional pain medications highlights ginger's efficacy in reducing pain while minimizing risks associated with prolonged use of NSAIDs. This makes ginger an appealing choice for individuals seeking natural pain management solutions.
By integrating ginger into your routine, you can harness its potential in reducing muscle pain and menstrual discomfort, further enhancing overall wellness and quality of life.
What Are the Antioxidant Effects of Ginger?
Ginger, renowned for its antioxidant-rich profile, offers substantial benefits in promoting overall wellness. The presence of gingerol, a potent antioxidant compound, is central to ginger's ability to combat oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. By neutralizing free radicals, gingerol helps protect cells from damage, which is crucial in preserving brain function and potentially safeguarding against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
The antioxidant effects of ginger extend to enhancing cognitive health. By reducing oxidative stress, ginger may improve brain function, supporting memory and cognitive processes. This makes ginger an appealing addition to diets focused on maintaining mental acuity and long-term brain health. Evidence from antioxidant research underscores ginger’s free radical–scavenging strength: a 2022 systematic review(5) showed ginger root outperformed many other extracts in neutralizing harmful radicals (like hydroxyl and superoxide) through multiple in vitro assays.
To maximize the protective antioxidant activities of ginger, consider incorporating it into your daily diet in various forms. Fresh ginger root can be grated into dishes, brewed as a tea, or blended into smoothies. For those seeking convenience, ginger supplements are available in capsule or powder forms, ensuring consistent intake of ginger's beneficial compounds.
By making ginger a staple in your diet, you can harness its antioxidant power to support overall wellness, promote brain health, and potentially reduce the risk of cognitive decline.

Final Words
Exploring the 5 benefits of ginger for your body reveals its versatile role in promoting health. Ginger's anti-inflammatory properties alleviate joint pain, while its digestive benefits ease nausea and improve stomach function.
Its immunity-boosting powers fight off common illnesses, and its pain-relieving effects offer natural alternatives to medications.
Moreover, ginger's antioxidant properties contribute to overall wellness by protecting against oxidative stress. By incorporating ginger into your diet, you can harness a natural ally for health and vitality, enhancing your daily wellness routine with its multifaceted benefits.
FAQ
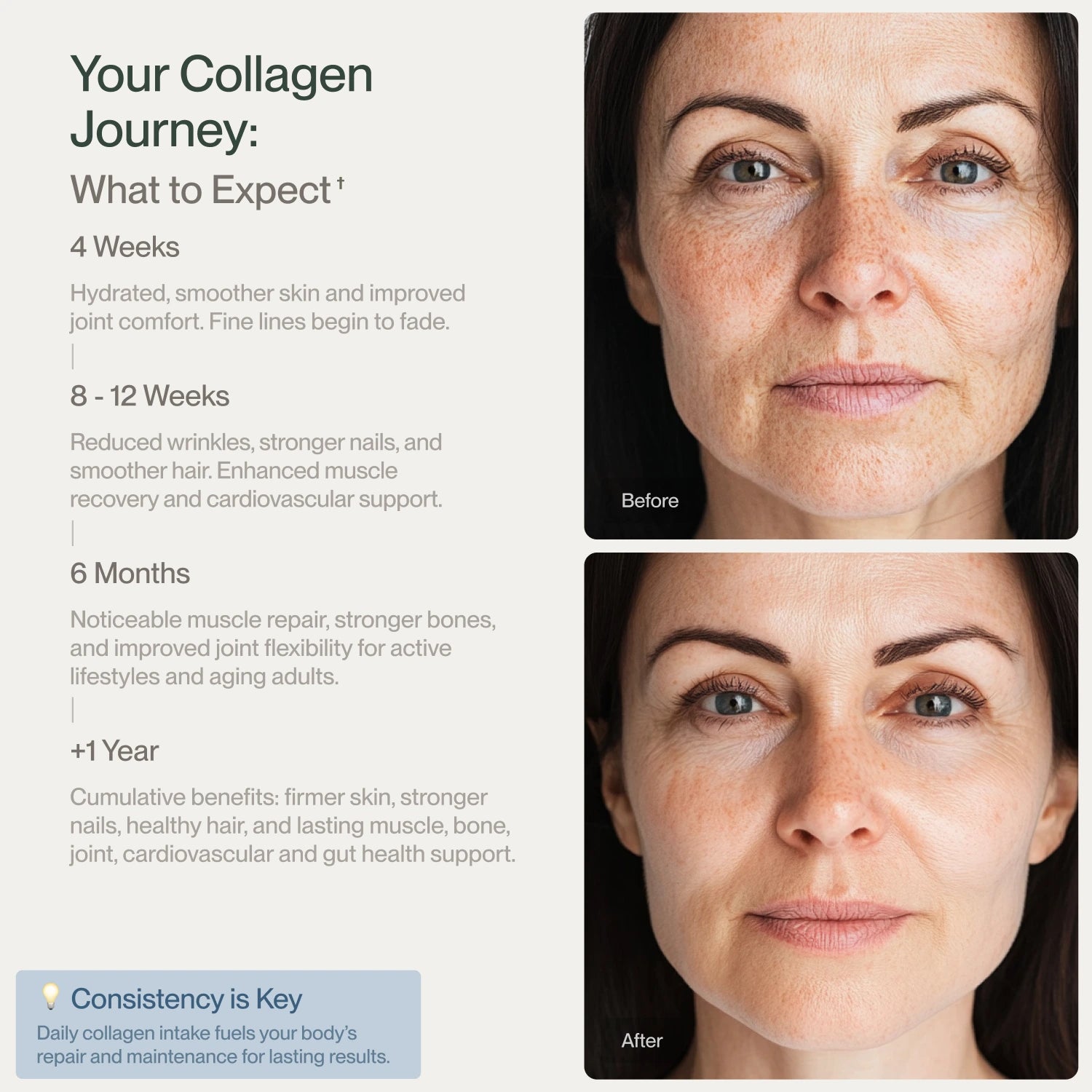
Is it beneficial to use ginger and collagen together?
Yes. Ginger’s anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce inflammation in joints and connective tissues. This can complement collagen supplements’ role in supporting joint health.
Does ginger improve collagen absorption?
Ginger does not directly increase collagen absorption; however, by improving circulation, it may help nutrients travel more efficiently throughout the body. This can enhance the visible and functional collagen benefits for skin and joints.
How can ginger and collagen be used together for skin health?
While collagen supports skin elasticity and hydration, ginger’s antioxidant properties help protect the skin from free radical damage. Using them together can offer a more comprehensive approach to skin care, especially for wrinkles and sagging skin concerns.
Can ginger help with collagen production?
Is it safe to take ginger and collagen supplements at the same time?
For most healthy adults, taking ginger and collagen together is safe and may even offer complementary benefits for joint, skin, and overall health. However, those with medical conditions or on certain medications should consult a healthcare professional.
How does ginger benefit men?
Ginger benefits men by supporting cardiovascular health, promoting weight management, and potentially improving testosterone levels, which can enhance overall vitality.
What happens if I take ginger every day?
Consuming ginger daily can lead to enhanced immune function, improved digestion, reduced inflammation, and relief from chronic pain, contributing to overall well-being.
What is the best form of ginger for health benefits?
Fresh ginger, ground ginger, and ginger tea are all effective forms that offer health benefits. The equation suggests choosing based on personal preference and specific health goals.
SOURCES
(1) - Hasani H, Arab A, Hadi A, Pourmasoumi M, Ghavami A, Miraghajani M. Does ginger supplementation lower blood pressure? A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Phytother Res. 2019 Jun;33(6):1639-1647. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6362. Epub 2019 Apr 11. PMID: 30972845.
(2) - Foshati, S., Po ursadeghfard, M., Heidari, Z. et al. The effects of ginger supplementation on common gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. BMC Complement Med Ther 23, 383 (2023).
(3) - Arcusa, R., Villaño, D., Marhuenda, J., Cano, M., Cerdà, B., & Zafrilla, P. (2022). Potential role of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) in the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9, Article ID 809621.
(4) - Broeckel, J.; Estes, L.; Leonard, M.; Dickerson, B.L.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Purpura, M.; Jäger, R.; Sowinski, R.J.; Rasmussen, C.J.; Kreider, R.B. Effects of Ginger Supplementation on Markers of Inflammation and Functional Capacity in Individuals with Mild to Moderate Joint Pain. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2365.
(5) - Ozkur, M., Benlier, N., Takan, I., Vasileiou, C., Georgakilas, A. G., Pavlopoulou, A., Cetin, Z., & Saygili, E. I. (2022). Ginger for healthy ageing: A systematic review on current evidence of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022, Article ID 4748447.
Scientifically Reviewed by Omer (Matt) Sermet