What is Collagen and Why is it Essential for Joint Function?
Collagen is a vital protein that forms the primary building blocks of connective tissues throughout the body, including cartilage, tendons, and ligaments that support our joints. Its unique fibrous structure provides strength, elasticity, and cushioning, enabling smooth, pain-free movement. Without adequate collagen, these tissues weaken, leading to stiffness, discomfort, and reduced mobility.
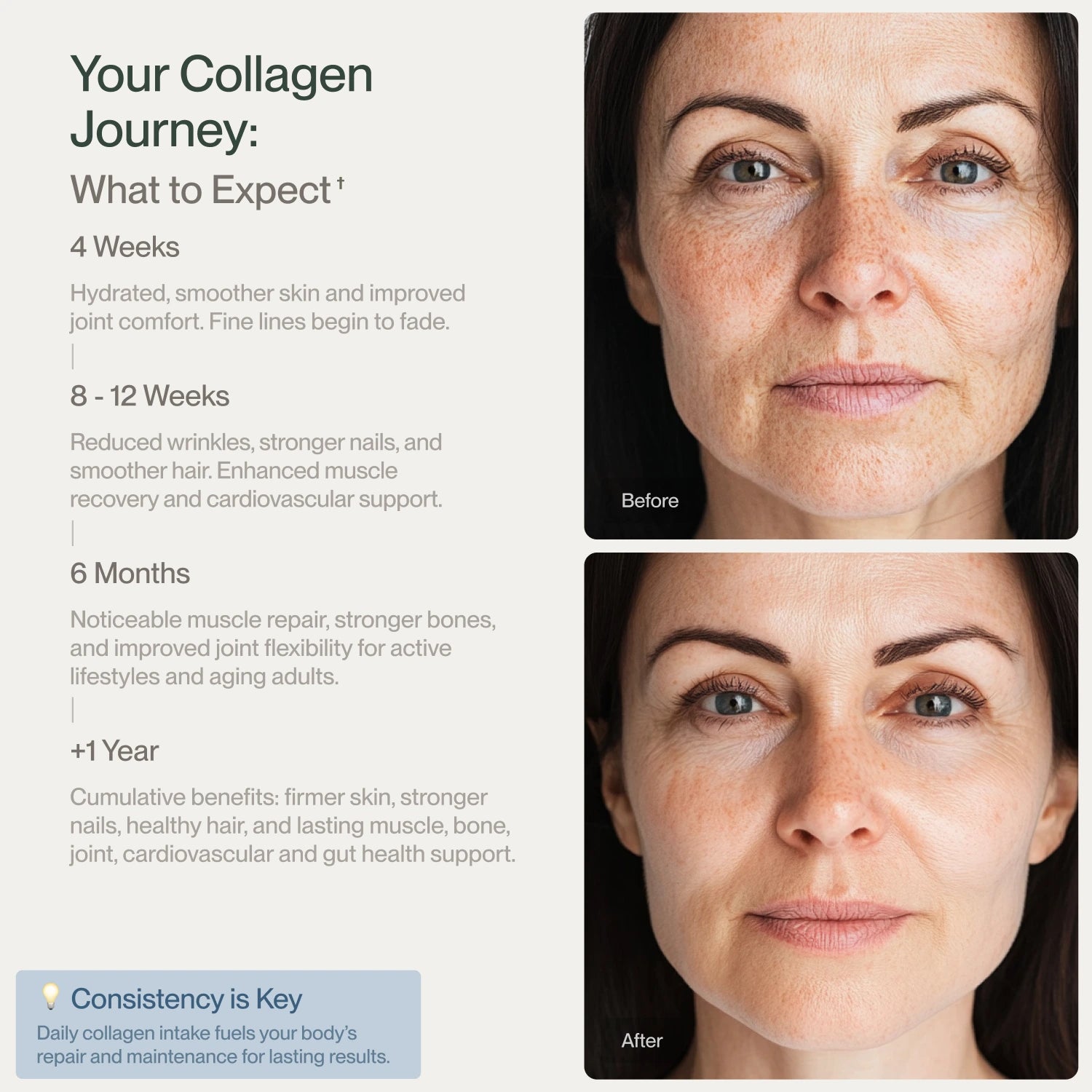
As we age, the body's natural collagen production decreases, typically starting around age 25 and accelerating after 60. This decline contributes to common joint issues like osteoarthritis, where cartilage degrades, causing bones to rub against each other. Restoring collagen levels through supplementation can help maintain the integrity of joint structures and mitigate these age-related effects.
How Does Collagen Support Healthy Joints and Reduce Discomfort?
Collagen supports joint health through several mechanisms, primarily by reinforcing the cartilage that cushions joints and by stimulating the body's own collagen production. Research indicates that collagen hydrolysate, a broken-down form of collagen, is absorbed by the digestive system and accumulates in cartilage, where it stimulates chondrocytes the cells responsible for cartilage synthesis. This process helps to repair and regenerate cartilage, leading to reduced joint pain and improved physical function.
Can Collagen Improve Joint Flexibility and Mobility for Athletes?
Yes, collagen can significantly improve joint flexibility and mobility, especially for athletes and active individuals. Intense physical activity often leads to joint stress and discomfort. Bioactive collagen peptides (BCPs) have been shown to support joint health and reduce activity-related pain. A 2017 study published in Applied Physiology(1), Nutrition and Metabolism found that daily supplementation with 5 grams of collagen peptides over 12 weeks significantly reduced knee joint discomfort during physical activity in 139 athletic participants compared to a placebo group. This suggests that collagen supplementation can be a valuable tool for athletes to maintain long-term joint function and mobility, aiding in recovery and preventing injuries.
How Does Collagen Help Combat Age-Related Joint Stiffness?
Collagen plays a crucial role in combating age-related joint stiffness by strengthening joint structures and promoting cartilage repair. As we age, wear and tear on joints can lead to stiffness, pain, and decreased mobility. Collagen supplementation helps by restoring diminished collagen reserves, promoting the repair of cartilage, and reducing inflammation. This comprehensive action strengthens joints against the effects of aging, allowing individuals to remain active and mobile.
Studies on heat shock proteins (HSPs), key molecular chaperones in stress response, reveal how cellular proteins adapt to protect vital tissues. HSP levels dynamically respond to acute stress to preserve cellular function, whereas HSP remains stable, providing a baseline of protection, according to Yanfen Cheng(2).
What Types of Collagen are Best for Joint Health?
When considering collagen supplements for joint health, understanding the different types is crucial. While Type I collagen is abundant in skin and tendons, Type II collagen is specifically the most beneficial for joints. Type II collagen is predominantly found in cartilage, where it maintains flexibility and cushioning. Its unique molecular structure provides tensile strength and resistance to compression, supporting the extracellular matrix of cartilage and preventing premature wear and tear. Type II collagen also interacts with the immune system to help prevent the breakdown of joint cartilage, leading to improved mobility and reduced joint pain.
Hydrolyzed collagen, which is broken down into smaller peptides, is another versatile option. It enhances absorption and can support both skin and joint health. For those primarily focused on joint health, products rich in Type II collagen are recommended. However, a combination of Type I and III collagen can also be beneficial for overall connective tissue health, including skin hydration and suppleness, alongside joint support.
How Can You Naturally Boost Collagen Production in Your Body?
Boosting your body's natural collagen production involves a combination of dietary and lifestyle adjustments. Simple changes can make a significant difference:
- Hydration: Drinking enough water is essential for overall cellular health and can indirectly support collagen synthesis.
- UV Protection: Limiting exposure to harmful UV rays helps protect existing collagen from damage.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate, regular exercise improves blood flow, delivering more oxygen and nutrients to joint areas, which supports collagen production.
- Vitamin C Intake: Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant crucial for collagen synthesis. Foods rich in vitamin C include oranges, strawberries, kiwis, and bell peppers.
- Zinc and Amino Acids: Zinc, glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline are vital building blocks for collagen. Incorporate foods like bone broth and gelatin, which are rich in collagen, to provide these essential amino acids.
Can Collagen Prevent Joint Pain in Aging Adults?
Yes, collagen can play a significant role in preventing and alleviating joint pain in aging adults. Collagen serves as both a therapeutic option for persistent joint pain and a common supplement recommended post-surgery. Collagen hydrolysate (CH) to mitigate activity-induced joint discomfort in physically active athletes according to Kristine L Clark(3). A study focused on young, active individuals offers insights into the potential advantages of collagen supplementation for adults in preventing or mitigating joint discomfort. 147 participants, with 97 completing the trial, and assessed parameters such as joint pain during rest, walking, standing, and lifting. Participants who received daily supplementation with 10g of collagen hydrolysate experienced statistically significant reductions in joint pain compared to the placebo group.
Collagen hydrolysate helps ease joint pain and increase mobility; it reduces discomfort and improves physical function in osteoarthritis patients in the short term, according to Xiaoqian Liu(4). In particular, older persons suffering from activity-related joint pain should expect a robust therapeutic benefit from the effect size.
Collagen and Tendon Health: A Closer Look
Beyond joints, collagen is also crucial for the strength and elasticity of tendons, which connect muscles to bones. Tendons are primarily composed of Type I collagen, enabling them to withstand significant forces during movement. Understanding how collagen supports tendon health is vital for athletes and active individuals seeking to prevent injuries and enhance recovery. For a deeper dive into this topic, explore our dedicated article: Collagen Supplements for Tendons
Collagen for Arthritis: Natural Approaches to Joint Pain Relief
Arthritis, characterized by joint inflammation, pain, and stiffness, often involves the degradation of cartilage. Collagen supplementation, particularly with collagen hydrolysate, has shown promise in stimulating cartilage regeneration and reducing inflammation associated with various forms of arthritis. By supporting the rebuilding of cartilage, collagen can help alleviate symptoms and improve mobility for those living with arthritis. Learn more about how collagen can offer natural relief for joint pain and mobility in our detailed article: Collagen for Arthritis: Natural Relief for Joint Pain and Mobility
Conclusion: Making an Informed Choice for Joint Health
Choosing the right collagen supplement is key to effectively supporting your joint health. The most effective collagen products for joints are those that stimulate chondrocytes, the main cells responsible for building and maintaining articular cartilage. By activating these cells, quality collagen supplements can help regenerate cartilage, reduce pain, and enhance mobility, allowing for a more active and pain-free lifestyle. Always look for products backed by scientific research that specifically target chondrocyte health and overall joint resilience.
SOURCES
(1) - Zdzieblik D, Oesser S, Gollhofer A, König D. Improvement of activity-related knee joint discomfort following supplementation of specific collagen peptides. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2017 Jun;42(6):588-595. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2016-0390. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Erratum in: Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2017 Nov;42(11):1237. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2017-0693. PMID: 28177710.
(2) - Cheng Y, Sun J, Chen H, Adam A, Tang S, Kemper N, Hartung J, Bao E. Expression and location of HSP60 and HSP10 in the heart tissue of heat-stressed rats. Exp Ther Med. 2016 Oct;12(4):2759-2765. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3650. Epub 2016 Sep 1. PMID: 27698781; PMCID: PMC5038565.
(3) - Clark KL, Sebastianelli W, Flechsenhar KR, Aukermann DF, Meza F, Millard RL, Deitch JR, Sherbondy PS, Albert A. 24-Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate as a dietary supplement in athletes with activity-related joint pain. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008 May;24(5):1485-96. doi: 10.1185/030079908x291967. Epub 2008 Apr 15. PMID: 18416885.
(4) - Liu X, Machado GC, Eyles JP, Ravi V, Hunter DJ. Dietary supplements for treating osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2018 Feb;52(3):167-175. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2016-097333. Epub 2017 Oct 10. PMID: 29018060.