What Are Some Probiotic Foods You Can Try?
Probiotic foods are an essential part of a balanced diet, offering numerous benefits for gut health thanks to their live cultures. Here are some examples of probiotic-rich foods you should consider:
- Yogurt: Made from milk fermented by lactic acid bacteria, yogurt is one of the most accessible and popular probiotic foods. It supports digestion and can improve lactose intolerance symptoms.
- Kefir: This fermented milk drink is similar to yogurt but contains a wider variety of bacterial and yeast strains, making it a powerhouse of probiotics. Kefir is beneficial for gut health and provides a creamy, tangy flavor.
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage, known as sauerkraut, is rich in probiotics and enzymes that aid digestion. It's a staple in many Eastern European cuisines and offers a tangy, crunchy addition to meals.
- Kimchi: A traditional Korean dish, kimchi is made by fermenting vegetables with spices and seasonings. This spicy treat is loaded with probiotics and is known for its digestive benefits and potential to boost the immune system.
- Miso: This Japanese seasoning is made from fermented soybeans and offers a savory, umami flavor. Miso is rich in probiotics and can be used in soups, dressings, and marinades.
- Kombucha: A fermented tea drink, kombucha contains a mix of bacteria and yeast, contributing to improved digestion and detoxification. It's a refreshing beverage option with a slightly effervescent quality.
A 10-week clinical trial conducted at Stanford University showed that regular consumption of fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, and kimchi increased gut microbiota diversity and reduced inflammation (Stanford Medicine, 2021)(1). Including these probiotic foods in your diet can enhance gut health and provide additional nutritional benefits. Each of these foods offers a unique taste and set of benefits, making them versatile options for improving overall wellness.
How Probiotic Foods Benefit Your Health?
Probiotic foods benefit your health by supporting and balancing the gut microbiome. These foods are rich in live cultures that bolster digestive health and may alleviate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and diarrhea, creating a healthier gut environment.
Probiotics are effective in strengthening the immune system and alleviating digestive disorders such as IBS and lactose intolerance, as highlighted in a comprehensive review published in 2024 in Microorganisms(2). They work by fostering a balance between helpful and harmful bacteria in the gut, which enhances the body’s ability to fend off infections and diseases. This support is particularly beneficial for individuals with weakened immune systems or during times of increased stress and illness.
Beyond digestive and immune support, probiotics may also offer benefits for skin health. By reducing inflammation and promoting a balanced gut microbiome, probiotics may improve conditions such as acne and eczema. Additionally, they might play a role in preventing allergies by modulating the body's immune response to allergens.
Here is a detailed overview of the benefits of various probiotic foods:
| Probiotic Food | Digestive Health | Immune Support | Skin Health | Allergy Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yogurt | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Kefir | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Sauerkraut | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Kimchi | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Miso | ✓ | |||
| Kombucha | ✓ | ✓ |
By incorporating these probiotic-rich foods into your diet, you can enhance your overall wellness, benefiting your digestive health and strengthening your immune system. The potential for improved skin health and allergy prevention further underscores the importance of these foods in a well-rounded diet.
Collagen and Probiotic: A Powerful Combination
Collagen peptides and probiotics each offer unique health benefits, but when combined, they create a powerful synergy that can significantly enhance overall wellness. Collagen peptides are known for their ability to improve skin elasticity and support joint health, providing essential amino acids crucial for cartilage repair and maintaining bone density. On the other hand, probiotics are vital for a healthy gut microbiome, promoting digestive health and boosting the immune system by balancing the good and bad bacteria in the gut.
The importance of probiotics lies in their ability to aid digestion and alleviate gastrointestinal issues like irritable bowel syndrome and diarrhea. They may also enhance skin health by reducing inflammation and potentially improving conditions such as acne. Moreover, probiotics can play a role in preventing allergies by modulating the immune response to allergens.
Combining collagen and probiotics can lead to improved skin health, offering both resilience and hydration, while also supporting joint flexibility and reducing inflammation. This combination may enhance gut health, leading to better nutrient absorption and a stronger immune system.
Below is a comparison table highlighting the complementary effects of collagen peptides and probiotics:
| Health Benefit | Collagen Peptides | Probiotics |
|---|---|---|
| Skin Elasticity | ✓ | |
| Joint Health | ✓ | |
| Digestive Health | ✓ | |
| Immune Support | ✓ | |
| Nutrient Absorption | ✓ | ✓ |
| Inflammation Reduction | ✓ | ✓ |
The integration of collagen and probiotic supplements into one's diet can offer a comprehensive approach to health. By addressing skin, joint, and digestive needs, this powerful combination provides a holistic strategy for enhancing well-being and maintaining a balanced lifestyle.
Tips for Incorporating Probiotics into Your Diet
Adding probiotics to your daily meals can significantly improve gut health naturally. Here are some practical tips to help you incorporate these beneficial bacteria into your diet:
- Start Slowly: Introduce probiotic foods gradually to allow your digestive system to adjust. Begin with small portions to minimize any potential gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Mix with Other Foods: To balance flavors and enhance enjoyment, incorporate probiotics into your meals. For example, add yogurt to smoothies or use kimchi as a flavorful topping for rice and salads.
- Check Labels: Ensure that the probiotic foods you select contain live cultures. Look for labels that specify "live and active cultures" to confirm the presence of beneficial bacteria.
- Diverse Choices: Include a variety of probiotic-rich foods such as kefir, sauerkraut, and miso. This diversity ensures you consume different strains of probiotics, each offering unique health benefits.
- Mind Added Sugars: Be cautious of products with high sugar content, as they can counteract the benefits of probiotics. Opt for unsweetened versions whenever possible.
-
Consistency is Key: For optimal results, incorporate probiotics into your diet consistently. Regular consumption helps maintain a balanced gut microbiome, supporting digestion and overall health.
By following these tips, you can effectively enhance your consumption of probiotics, incorporating gut-friendly foods into your daily routine and promoting a healthier digestive system.
Final Words
Exploring probiotic foods opens a path to enhanced digestive and immune health. With examples such as yogurt, kefir, and kimchi, these foods bolster gut balance and overall well-being. Probiotic foods like sauerkraut and miso are imbued with beneficial bacteria crucial for gut microbiome support.
Combining probiotics with collagen offers a comprehensive approach to health, improving skin, joint, and digestive wellness. By incorporating these foods wisely, you can naturally bolster your health. Embrace probiotic foods for a brighter, healthier lifestyle journey.
FAQ
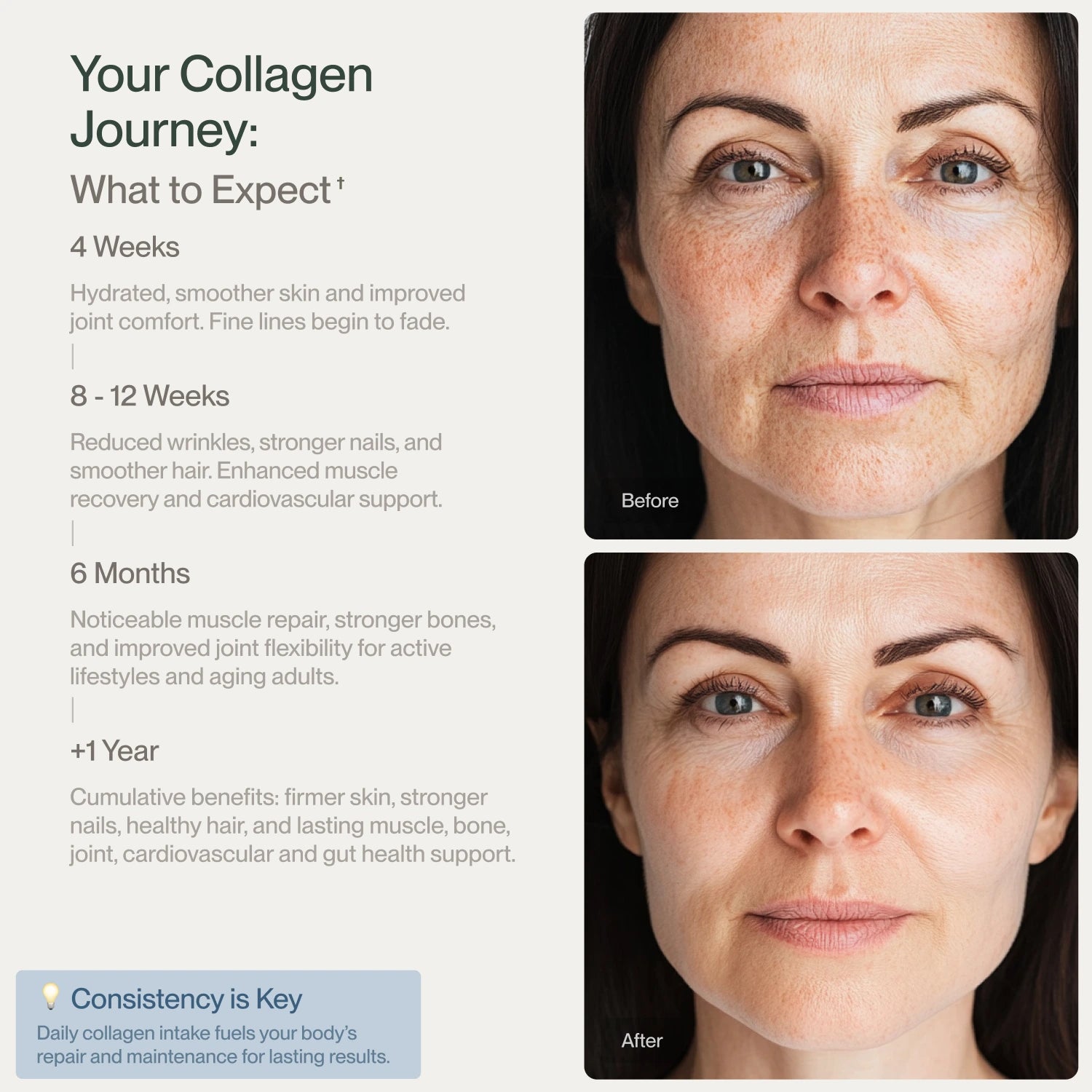
How long does it take to see the effects of collagen?
Many people wonder, how long does it take for collagen to work? With regular use, noticeable improvements in skin elasticity can appear within 4-8 weeks, while hair and nail health may benefit within 2-3 months. Joint health improvements may take a few months as well. Individual results vary depending on age, diet, and lifestyle.
Which foods can support collagen intake?
To boost collagen production, consuming collagen with vitamin C is highly effective, as vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis (e.g., oranges, red peppers). Additionally, probiotics support gut health and improve collagen absorption, and protein-rich foods provide amino acids needed for collagen production (e.g., eggs, fish, chicken).
Are there any side effects of collagen supplements?
Collagen is generally safe, and serious side effects are rare. Some people may experience mild digestive discomfort, bloating, or nausea. Taking collagen with probiotics can help improve digestive comfort and reduce the risk of minor side effects.
SOURCES
(1) - Weaver, J. (2021, 12 Temmuz). Fermented-food diet increases microbiome diversity, decreases inflammatory proteins, study finds. Stanford Medicine News Center.
(2) - Maftei, N.-M.; Raileanu, C.R.; Balta, A.A.; Ambrose, L.; Boev, M.; Marin, D.B.; Lisa, E.L. The Potential Impact of Probiotics on Human Health: An Update on Their Health-Promoting Properties. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 234.
Scientifically Reviewed by Omer (Matt) Sermet