How to Determine Your Daily Protein Requirements?
Your daily protein needs depend on both your body weight and activity level. The general guideline, known as the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)(1), suggests 0.36 ounces of protein per pound of body weight per day (0.8 g per kg) for sedentary adults. However, if you exercise regularly or aim to build muscle, your protein requirements increase. According to the American College of Sports Medicine(2), active individuals may need 0.54–0.91 ounces per pound (1.2–2.0 g per kg) to support muscle repair and growth.
Protein Intake by Activity Level
In this table, you can quickly see how activity level impacts protein needs. For example, a sedentary person weighing 154 lbs (70 kg) requires about 2.52 oz (56 g) of protein daily, while an athlete of the same weight may need up to 6.30 oz (140 g).
| Activity Level | Protein Intake (oz/lb/day) (g/kg/day) | Example for 154 lbs (70 kg) person |
|---|---|---|
| Sedentary (little to no exercise) | 0.36 oz (0.8 g) | 2.52 oz (56 g) |
| Moderate exercise | 0.54 – 0.73 oz (1.2 – 1.6 g) | 3.78 – 5.04 oz (84 – 112 g) |
| Intense training / Athletes | 0.73 – 0.91 oz (1.6 – 2.0 g) | 5.04 – 6.30 oz (112 – 140 g) |
How to Calculate Your Protein Needs
- Find your weight in pounds.
- Multiply by the recommended intake based on your activity level.
Example:
154 lbs × 0.54 = 83.16 g → ~3.78 oz (moderate activity)
154 lbs × 0.91 = 140 g → ~6.30 oz (intense training)
It's important to balance your protein intake with other macronutrients to ensure a well-rounded diet. Protein needs can also vary based on individual health goals, age, and specific dietary requirements. Adjustments should be made based on any changes in activity level or health objectives to ensure optimal protein intake.
How Much Protein is Needed for Muscle Gain and Weight Loss?
Reaching goals like muscle gain or weight loss requires a smart approach to protein intake. For muscle building, especially among athletes or bodybuilders, consuming 2–3 times the RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) can be highly beneficial. This equals roughly 0.73–1.09 oz per pound of body weight (1.6–2.4 g per kg), which is much higher than the standard 0.36 oz per pound (0.8 g per kg) recommended for sedentary adults. This higher amount supports muscle repair and growth after intense workouts.
Protein for Weight Loss
Protein also plays a vital role in weight loss:
- Helps preserve lean muscle mass while in a calorie deficit.
- Increases satiety, reducing overall calorie intake.
- The Food and Nutrition Board recommends protein to make up 10–35% of total daily calories, giving flexibility for different diet styles.
Example: Calculating Protein Needs
- For Muscle Gain:
For muscle gain, a person weighing 154 lbs (70 kg) and engaging in regular resistance training may need 3.95 – 5.93 oz (112 – 168 g) of protein per day, depending on workout intensity and goals.
General athletes: 3.95 – 4.94 oz (112 – 140 g)
Advanced bodybuilders: 4.94 – 5.93 oz (140 – 168 g)
- For Weight Loss:
The Food and Nutrition Board(3) suggests that protein should constitute 10 to 35% of total daily calories. So keep protein intake at the upper end of the 10–35% range of daily calories to control hunger and protect muscle mass during fat loss.
Quick Reference Table
In this table, you can see how protein requirements increase for muscle building or weight loss compared to general health needs.
| Goal | Protein Intake (oz/lb/day) (g/kg/day) | Example for 154 lbs (70 kg) |
|---|---|---|
| General health (RDA) | 0.36 oz (0.8 g) | 2.52 oz (56 g) |
| Muscle gain – general athletes | 0.73 – 0.91 oz (1.6 – 2.0 g) | 3.95 – 4.94 oz (112 – 140 g) |
| Muscle gain – advanced bodybuilders | 0.91 – 1.09 oz (2.0 – 2.4 g) | 4.94 – 5.93 oz (140 – 168 g) |
| Weight loss (upper target) | 0.82 – 1.0 oz (1.8 – 2.2 g) | 4.48 – 5.60 oz (126 – 158 g) |
Balancing protein intake with healthy fats and carbohydrates is essential to ensure nutritional adequacy. It’s important to distribute protein consumption evenly across meals to optimize muscle protein synthesis and maintain energy levels throughout the day. This approach not only supports physical goals but also promotes overall health and well-being.
How Do Protein Needs Vary by Age and Gender?
Protein requirements vary based on age, gender, and life stage. As we get older, maintaining muscle mass and bone health becomes even more important, so protein intake often needs to be adjusted. Below is a summary of general guidelines:
| Age Group | Gender | Recommended Intake | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adults (18–65) | Women | 1.2 oz per day (45 g) – about 0.36 oz/lb (0.8 g/kg) | Baseline for basic physiological functions. |
| Men | 1.95 oz per day (55.5 g) – about 0.36 oz/lb (0.8 g/kg) | Slightly higher due to greater lean body mass. | |
| Adults (65+) | Both | 0.54 oz/lb (1.2 g/kg) | Higher intake helps preserve muscle mass, bone density, and joint health. |
Which Protein Sources Are High Quality?
High-quality protein sources are essential for a balanced diet, supporting muscle maintenance, repair, and overall health. Both animal and plant-based foods offer rich protein content, each with unique nutritional benefits.
Animal-based protein sources such as chicken, fish, and dairy products provide complete proteins, containing all essential amino acids necessary for the body's needs. Chicken, in particular, is a versatile and lean source of protein that can be easily incorporated into various meals. Fish not only offers high-quality protein but also supplies omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
Plant-based protein sources are equally valuable and include legumes, tofu, seeds, and nuts. These options are not only rich in protein but also packed with fiber, vitamins, and unsaturated fats, which contribute to overall wellness. Legumes such as lentils and chickpeas are excellent protein sources that can enhance dietary variety, especially for vegetarians and vegans.
Tofu, made from soybeans, is another plant-based protein that is versatile and can be used in numerous dishes to replace meat. Seeds and nuts, while high in protein, also provide essential fatty acids and nutrients that support cardiovascular health.
Incorporating a range of these protein sources into daily meals ensures a balanced intake of essential nutrients. The combination of animal and plant-based proteins can help meet dietary needs while promoting a healthy lifestyle and supporting muscle growth and repair.

The Complementary Roles of Protein and Collagen
Protein and collagen, while both essential proteins, play distinct yet complementary roles in maintaining overall health and vitality. Protein, as a macronutrient, is fundamental for muscle repair, growth, and various metabolic functions. It provides the building blocks (amino acids) necessary for synthesizing new tissues, enzymes, and hormones, crucial for energy production and overall bodily function.
Collagen, on the other hand, is the most abundant structural protein in the human body. It forms the primary component of connective tissues, including skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. Its unique triple-helix structure provides strength, elasticity, and integrity to these tissues. While dietary protein contributes to the general pool of amino acids, specific collagen peptides are particularly effective in supporting the body's natural collagen production.
The synergy between protein and collagen is vital for comprehensive wellness. Adequate protein intake ensures that the body has the necessary amino acids for all its protein synthesis needs, including collagen. Simultaneously, direct collagen supplementation, such as with Collavita Collagen, provides specific peptides that can directly support skin elasticity, joint health, and the strength of connective tissues. This combined approach optimizes the body's ability to maintain structural integrity and functional efficiency, contributing to a more youthful appearance, improved mobility, and enhanced overall well-being.
When and How Should Protein Supplements Be Used?
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Who Benefits Most? | - Athletes and individuals with intense training - People with higher-than-average protein needs |
| Forms | - Protein powders - Protein bars - Protein shakes |
| When to Use | - Post-workout: for fast absorption to support muscle repair and growth - When daily protein intake from whole foods falls short |
| How to Use | - Use a protein calculator to determine needs - Fill the gap with supplements, not replace meals - Integrate with balanced meals rather than rely solely on them |
| Advantages | - Convenient and practical - Rapid absorption (especially whey protein) - Helps meet daily protein requirements |
| Risks / Cautions | - Excess protein → converted to energy or stored as fat - Over-reliance on supplements → risk of missing vitamins/minerals found in whole foods |
| Balance with Whole Foods | - Prioritize natural protein sources (meat, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes) - Whole foods provide extra nutrients (fiber, vitamins, minerals) that supplements lack |
FAQ
Is consuming too much protein harmful?
For most healthy individuals, excess protein is not harmful, but balance is key. Alongside protein, consider nutrients like collagen, which supports joints and tissues without adding strain to your diet.
Are protein powders only for athletes?
Not at all. Protein powders help anyone meet daily needs. Similarly, collagen powders are widely used not just for beauty, but also to aid joint health and recovery for active lifestyles.
Can vegans get enough protein?
Yes, vegans can get enough protein by combining legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds, which together provide all the essential amino acids. Especially when it comes to collagen alternatives, instead of relying on animal-based collagen, they can support the body’s natural production with nutrients like vitamin C, zinc, and specific amino acids. This way, protein needs are met while also promoting healthy skin, joints, and connective tissues.
How should I distribute my protein intake throughout the day?
Spreading protein across meals optimizes absorption. Likewise, adding Collavita Collagen to your morning routine or post-workout shake can support muscle recovery, joint comfort, and skin vitality throughout the day.
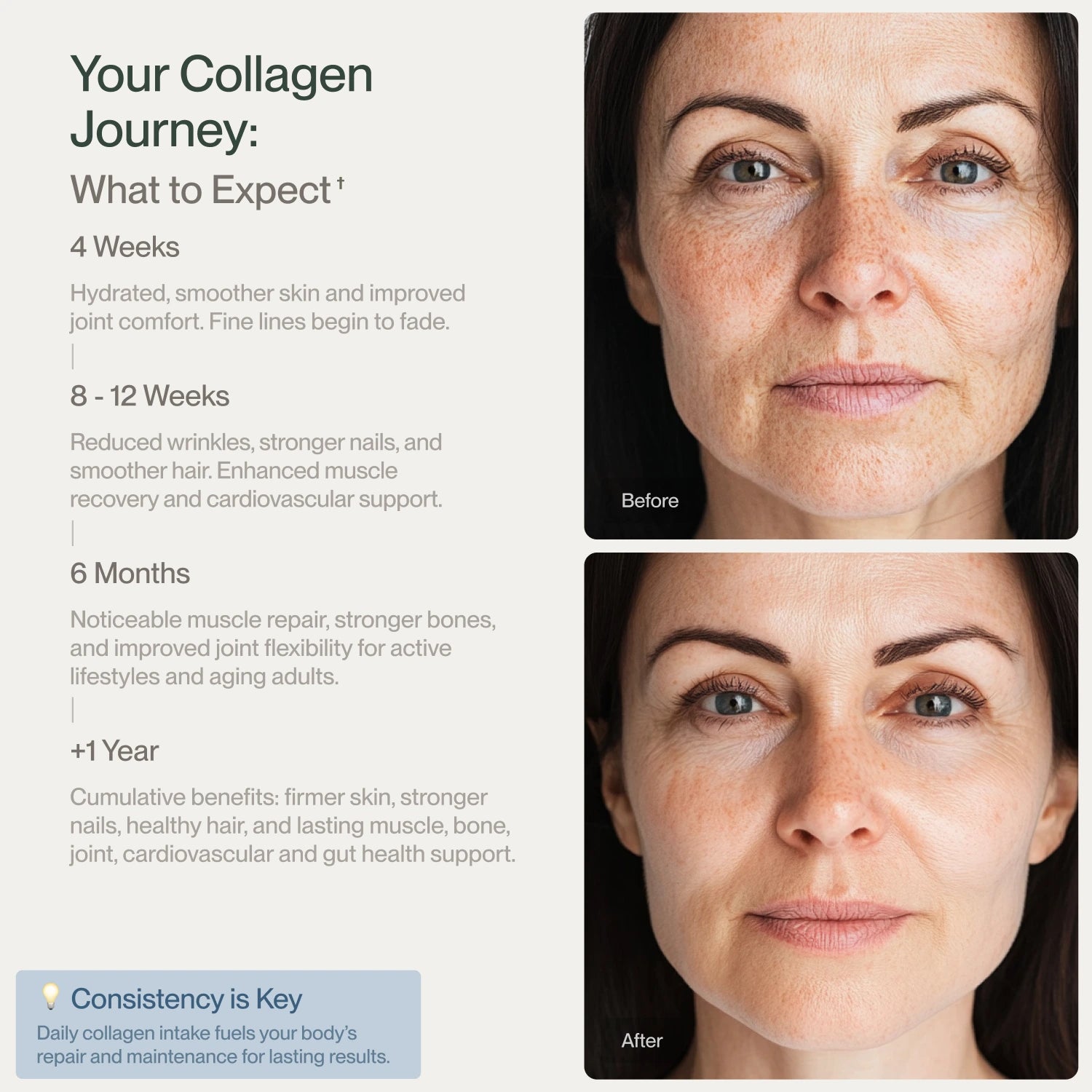
How Can Collagen Improve Overall Wellness?
Collagen plays a key role in overall wellness by supporting skin elasticity, joint health, and muscle recovery. The collagen benefits include strengthening connective tissues, reducing joint discomfort, and enhancing skin appearance, leading to a more youthful look. Regular collagen intake can improve mobility and support joint and bone health.
SOURCES
(1) - Rodriguez, N. (2024). The emerging science of rehabilitative nutrition: Protein’s role as the protagonist
(2) - Vitale K, Getzin A. Nutrition and Supplement Update for the Endurance Athlete: Review and Recommendations. Nutrients. 2019 Jun 7;11(6):1289. doi: 10.3390/nu11061289. PMID: 31181616; PMCID: PMC6628334.
(3) - Manore MM. Exercise and the Institute of Medicine recommendations for nutrition. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2005 Aug;4(4):193-8. doi: 10.1097/01.csmr.0000306206.72186.00. PMID: 16004827.
Scientifically Reviewed by Omer (Matt) Sermet